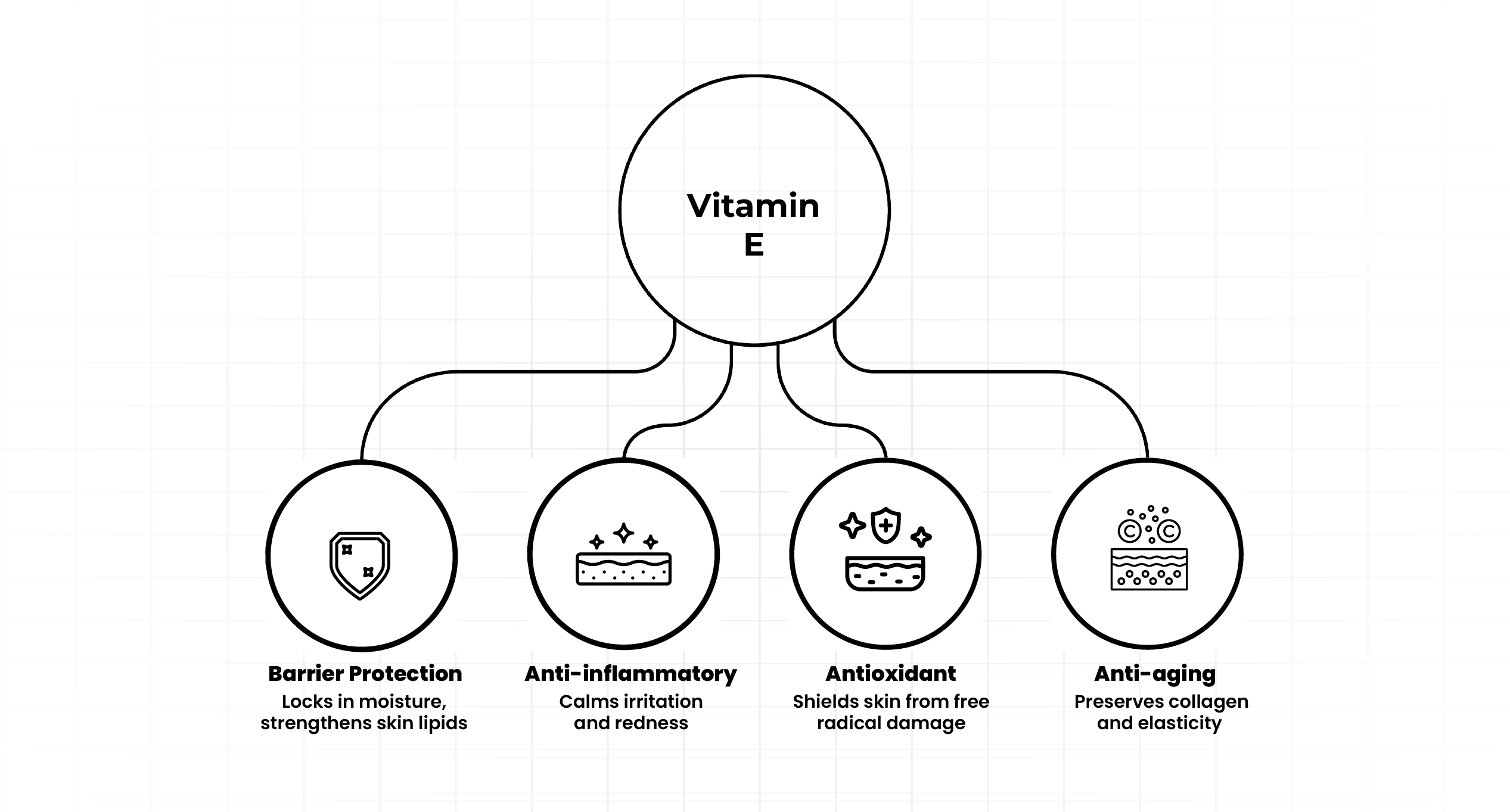
Vitamin E (α-tocopherol)
Oxidative stress from intrinsic factors (low antioxidant defenses) and extrinsic factors (UV exposure) drives skin aging by causing DNA damage, telomere shortening, lipid peroxidation, and collagen loss. These processes trigger inflammation, barrier disruption, and reduced elasticity, leading to dryness, pigmentation, and wrinkles. Tocotrienols, as potent Vitamin E isoforms, inhibit these oxidative pathways, preserving collagen, barrier integrity, and overall skin health.